This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
Two-phased Canary Rollout with Open Source Gloo
Author: Rick Ducott | GitHub | Twitter
Every day, my colleagues and I are talking to platform owners, architects, and engineers who are using Gloo as an API gateway to expose their applications to end users. These applications may span legacy monoliths, microservices, managed cloud services, and Kubernetes clusters. Fortunately, Gloo makes it easy to set up routes to manage, secure, and observe application traffic while supporting a flexible deployment architecture to meet the varying production needs of our users.
Beyond the initial set up, platform owners frequently ask us to help design the operational workflows within their organization: How do we bring a new application online? How do we upgrade an application? How do we divide responsibilities across our platform, ops, and development teams?
In this post, we're going to use Gloo to design a two-phased canary rollout workflow for application upgrades:
- In the first phase, we'll do canary testing by shifting a small subset of traffic to the new version. This allows you to safely perform smoke and correctness tests.
- In the second phase, we'll progressively shift traffic to the new version, allowing us to monitor the new version under load, and eventually, decommission the old version.
To keep it simple, we're going to focus on designing the workflow using open source Gloo, and we're going to deploy the gateway and application to Kubernetes. At the end, we'll talk about a few extensions and advanced topics that could be interesting to explore in a follow up.
Initial setup
To start, we need a Kubernetes cluster. This example doesn't take advantage of any cloud specific
features, and can be run against a local test cluster such as minikube.
This post assumes a basic understanding of Kubernetes and how to interact with it using kubectl.
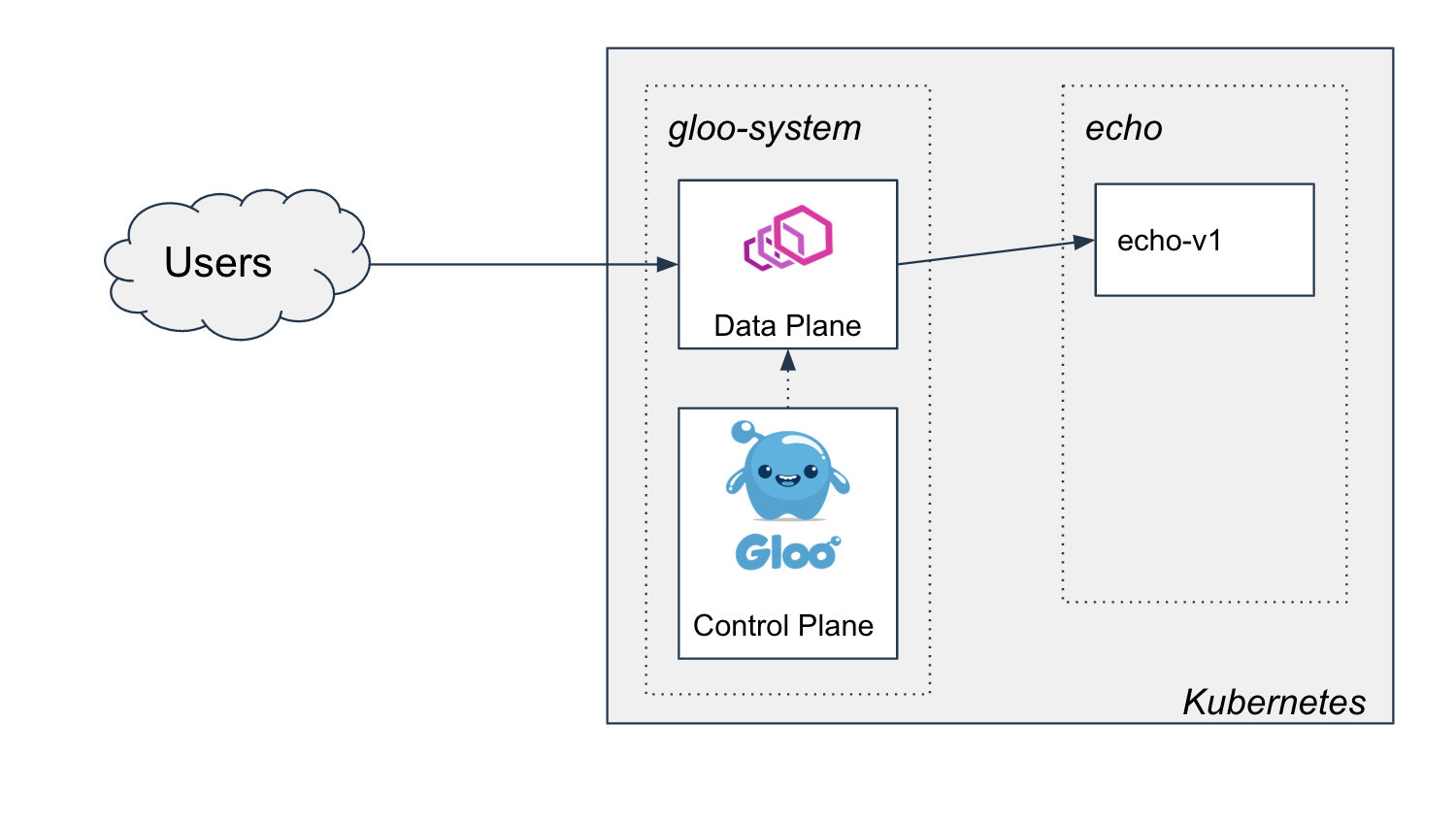
We'll install the latest open source Gloo to the gloo-system namespace and deploy
version v1 of an example application to the echo namespace. We'll expose this application outside the cluster
by creating a route in Gloo, to end up with a picture like this:
Deploying Gloo
We'll install gloo with the glooctl command line tool, which we can download and add to the PATH with the following
commands:
curl -sL https://run.solo.io/gloo/install | sh
export PATH=$HOME/.gloo/bin:$PATH
Now, you should be able to run glooctl version to see that it is installed correctly:
➜ glooctl version
Client: {"version":"1.3.15"}
Server: version undefined, could not find any version of gloo running
Now we can install the gateway to our cluster with a simple command:
glooctl install gateway
The console should indicate the install finishes successfully:
Creating namespace gloo-system... Done.
Starting Gloo installation...
Gloo was successfully installed!
Before long, we can see all the Gloo pods running in the gloo-system namespace:
➜ kubectl get pod -n gloo-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
discovery-58f8856bd7-4fftg 1/1 Running 0 13s
gateway-66f86bc8b4-n5crc 1/1 Running 0 13s
gateway-proxy-5ff99b8679-tbp65 1/1 Running 0 13s
gloo-66b8dc8868-z5c6r 1/1 Running 0 13s
Deploying the application
Our echo application is a simple container (thanks to our friends at HashiCorp) that will
respond with the application version, to help demonstrate our canary workflows as we start testing and
shifting traffic to a v2 version of the application.
Kubernetes gives us a lot of flexibility in terms of modeling this application. We'll adopt the following conventions:
- We'll include the version in the deployment name so we can run two versions of the application side-by-side and manage their lifecycle differently.
- We'll label pods with an app label (
app: echo) and a version label (version: v1) to help with our canary rollout. - We'll deploy a single Kubernetes
Servicefor the application to set up networking. Instead of updating this or using multiple services to manage routing to different versions, we'll manage the rollout with Gloo configuration.
The following is our v1 echo application:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: echo-v1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: echo
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: echo
version: v1
spec:
containers:
# Shout out to our friends at Hashi for this useful test server
- image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=version:v1"
- -listen=:8080
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: echo-v1
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
And here is the echo Kubernetes Service object:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: echo
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: echo
For convenience, we've published this yaml in a repo so we can deploy it with the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/1-setup/echo.yaml
We should see the following output:
namespace/echo created
deployment.apps/echo-v1 created
service/echo created
And we should be able to see all the resources healthy in the echo namespace:
➜ kubectl get all -n echo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/echo-v1-66dbfffb79-287s5 1/1 Running 0 6s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/echo ClusterIP 10.55.252.216 <none> 80/TCP 6s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/echo-v1 1/1 1 1 7s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/echo-v1-66dbfffb79 1 1 1 7s
Exposing outside the cluster with Gloo
We can now expose this service outside the cluster with Gloo. First, we'll model the application as a Gloo Upstream, which is Gloo's abstraction for a traffic destination:
apiVersion: gloo.solo.io/v1
kind: Upstream
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
kube:
selector:
app: echo
serviceName: echo
serviceNamespace: echo
servicePort: 8080
subsetSpec:
selectors:
- keys:
- version
Here, we're setting up subsets based on the version label. We don't have to use this in our routes, but later
we'll start to use it to support our canary workflow.
We can now create a route to this upstream in Gloo by defining a Virtual Service:
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
We can apply these resources with the following commands:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/1-setup/upstream.yaml
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/1-setup/vs.yaml
Once we apply these two resources, we can start to send traffic to the application through Gloo:
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
Our setup is complete, and our cluster now looks like this:

Two-Phased Rollout Strategy
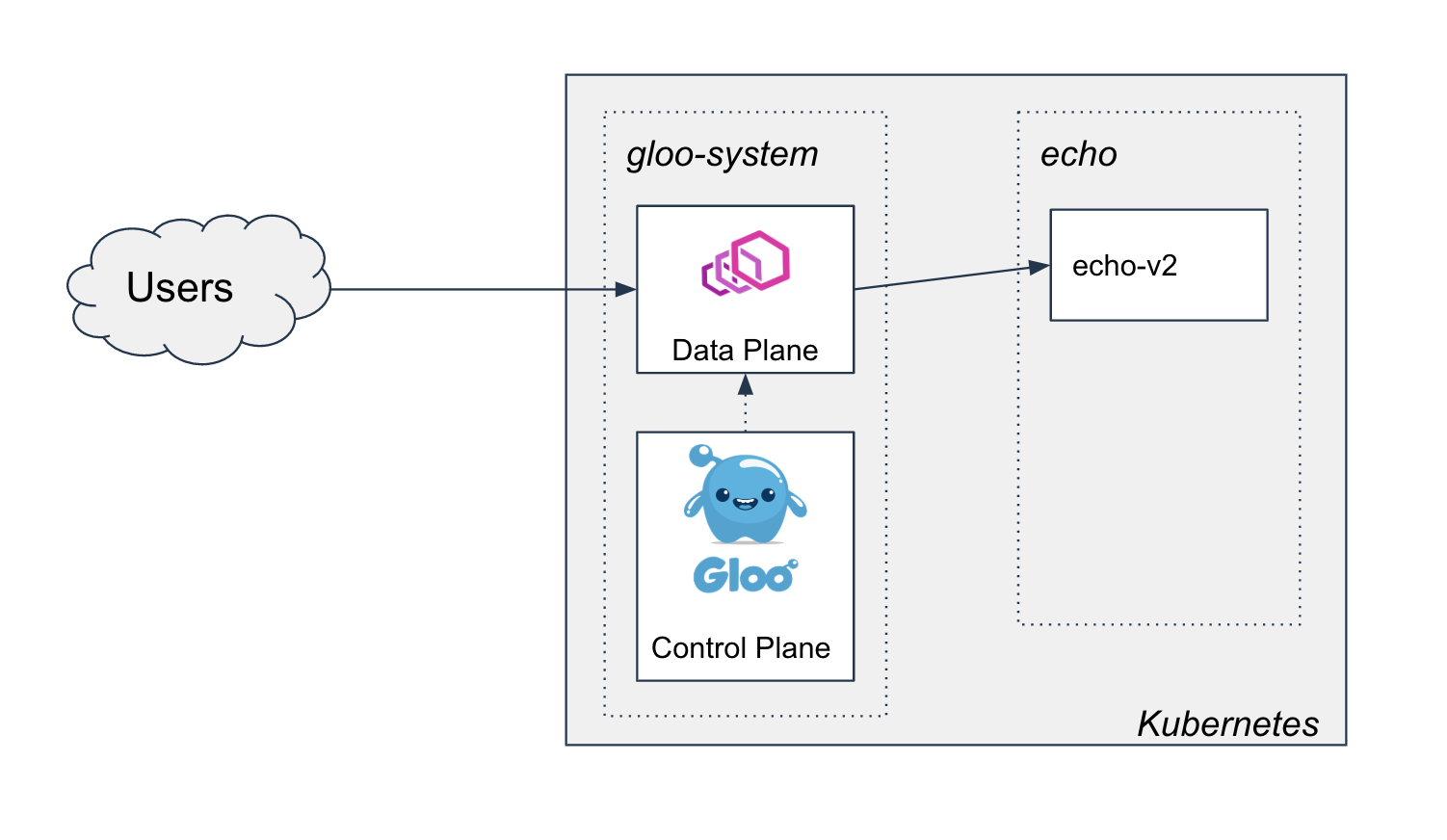
Now we have a new version v2 of the echo application that we wish to roll out. We know that when the
rollout is complete, we are going to end up with this picture:
However, to get there, we may want to perform a few rounds of testing to ensure the new version of the application meets certain correctness and/or performance acceptance criteria. In this post, we'll introduce a two-phased approach to canary rollout with Gloo, that could be used to satisfy the vast majority of acceptance tests.
In the first phase, we'll perform smoke and correctness tests by routing a small segment of the traffic to the new version
of the application. In this demo, we'll use a header stage: canary to trigger routing to the new service, though in
practice it may be desirable to make this decision based on another part of the request, such as a claim in a verified JWT.
In the second phase, we've already established correctness, so we are ready to shift all of the traffic over to the new version of the application. We'll configure weighted destinations, and shift the traffic while monitoring certain business metrics to ensure the service quality remains at acceptable levels. Once 100% of the traffic is shifted to the new version, the old version can be decommissioned.
In practice, it may be desirable to only use one of the phases for testing, in which case the other phase can be skipped.
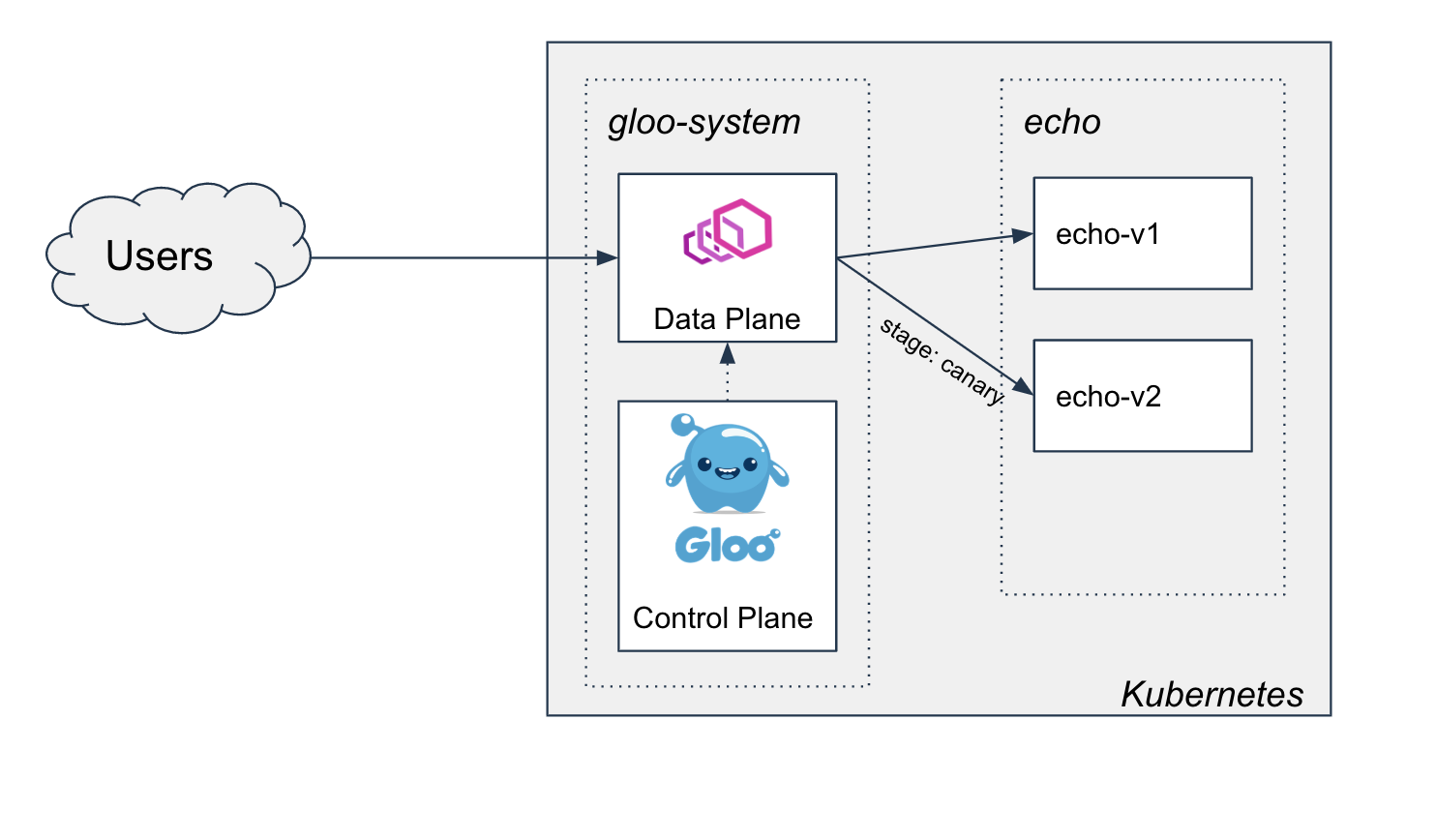
Phase 1: Initial canary rollout of v2
In this phase, we'll deploy v2, and then use a header stage: canary to start routing a small amount of specific
traffic to the new version. We'll use this header to perform some basic smoke testing and make sure v2 is working the
way we'd expect:
Setting up subset routing
Before deploying our v2 service, we'll update our virtual service to only route to pods that have the subset label
version: v1, using a Gloo feature called subset routing.
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v1
We can apply them to the cluster with the following commands:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/2-initial-subset-routing-to-v2/vs-1.yaml
The application should continue to function as before:
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
Deploying echo v2
Now we can safely deploy v2 of the echo application:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: echo-v2
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: echo
version: v2
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: echo
version: v2
spec:
containers:
- image: hashicorp/http-echo
args:
- "-text=version:v2"
- -listen=:8080
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: echo-v2
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
We can deploy with the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/2-initial-subset-routing-to-v2/echo-v2.yaml
Since our gateway is configured to route specifically to the v1 subset, this should have no effect. However, it does enable
v2 to be routable from the gateway if the v2 subset is configured for a route.
Make sure v2 is running before moving on:
➜ kubectl get pod -n echo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
echo-v1-66dbfffb79-2qw86 1/1 Running 0 5m25s
echo-v2-86584fbbdb-slp44 1/1 Running 0 93s
The application should continue to function as before:
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
Adding a route to v2 for canary testing
We'll route to the v2 subset when the stage: canary header is supplied on the request. If the header isn't
provided, we'll continue to route to the v1 subset as before.
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- matchers:
- headers:
- name: stage
value: canary
prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v1
We can deploy with the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/2-initial-subset-routing-to-v2/vs-2.yaml
Canary testing
Now that we have this route, we can do some testing. First let's ensure that the existing route is working as expected:
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
And now we can start to canary test our new application version:
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/ -H "stage: canary"
version:v2
Advanced use cases for subset routing
We may decide that this approach, using user-provided request headers, is too open. Instead, we may want to restrict canary testing to a known, authorized user.
A common implementation of this that we've seen is for the canary route to require a valid JWT that contains a specific claim to indicate the subject is authorized for canary testing. Enterprise Gloo has out of the box support for verifying JWTs, updating the request headers based on the JWT claims, and recomputing the routing destination based on the updated headers. We'll save that for a future post covering more advanced use cases in canary testing.
Phase 2: Shifting all traffic to v2 and decommissioning v1
At this point, we've deployed v2, and created a route for canary testing. If we are satisfied with the
results of the testing, we can move on to phase 2 and start shifting the load from v1 to v2. We'll use
weighted destinations
in Gloo to manage the load during the migration.
Setting up the weighted destinations
We can change the Gloo route to route to both of these destinations, with weights to decide how much of the traffic should
go to the v1 versus the v2 subset. To start, we're going to set it up so 100% of the traffic continues to get routed to the
v1 subset, unless the stage: canary header was provided as before.
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
# We'll keep our route from before if we want to continue testing with this header
- matchers:
- headers:
- name: stage
value: canary
prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
# Now we'll route the rest of the traffic to the upstream, load balanced across the two subsets.
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
multi:
destinations:
- destination:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v1
weight: 100
- destination:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
weight: 0
We can apply this virtual service update to the cluster with the following commands:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/3-progressive-traffic-shift-to-v2/vs-1.yaml
Now the cluster looks like this, for any request that doesn't have the stage: canary header:
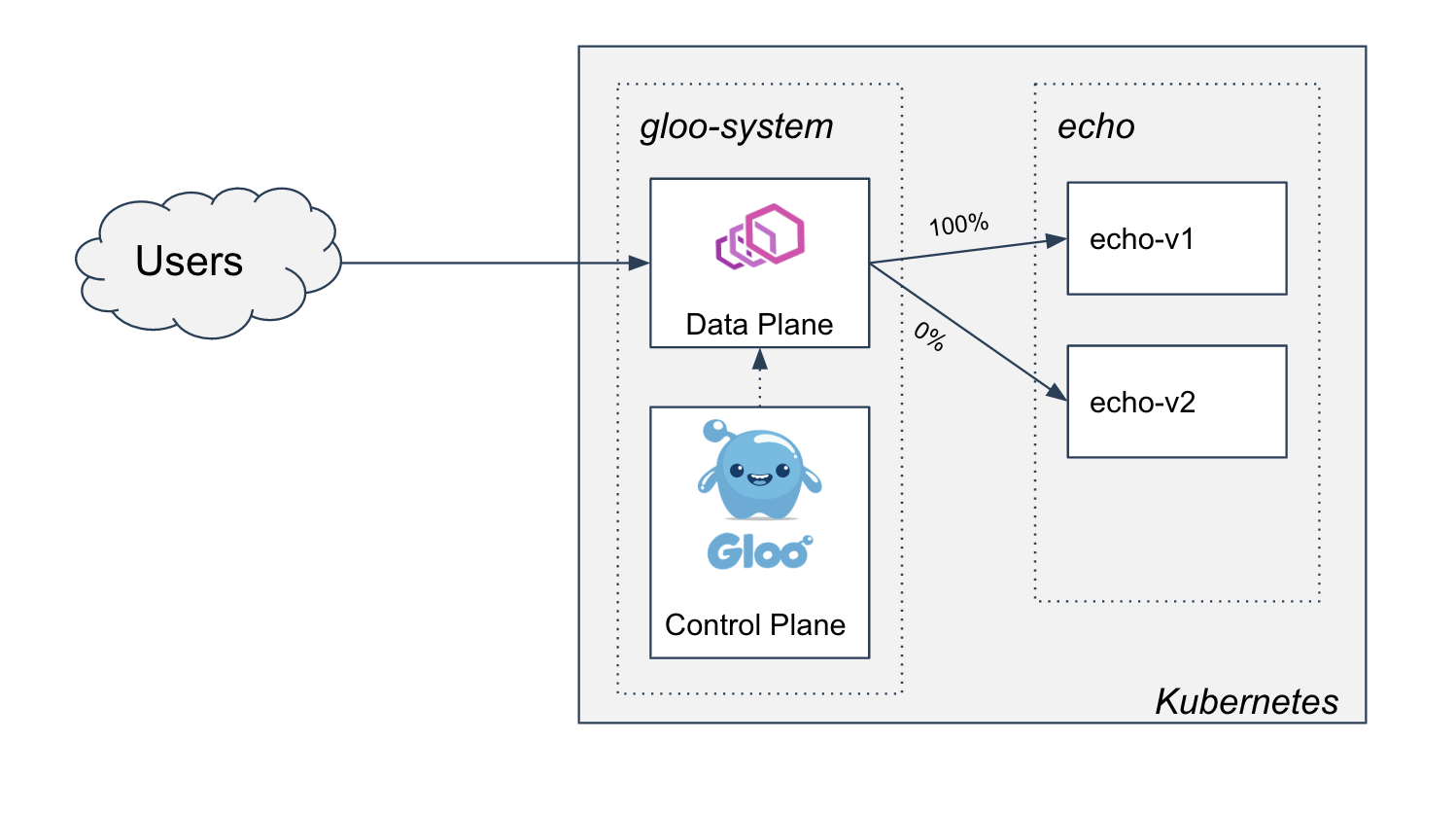
With the initial weights, we should see the gateway continue to serve v1 for all traffic.
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
Commence rollout
To simulate a load test, let's shift half the traffic to v2:
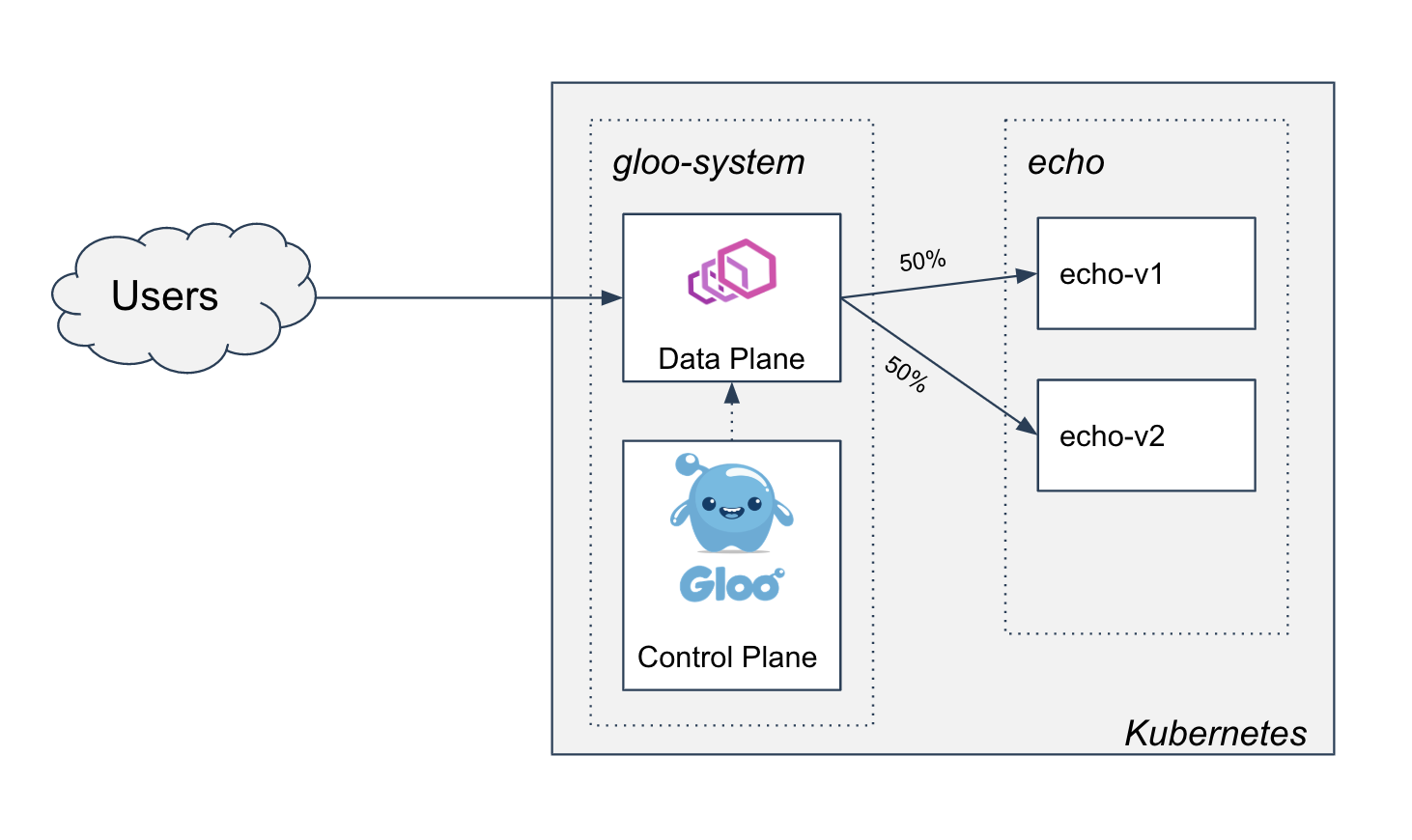
This can be expressed on our virtual service by adjusting the weights:
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- matchers:
- headers:
- name: stage
value: canary
prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
multi:
destinations:
- destination:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v1
# Update the weight so 50% of the traffic hits v1
weight: 50
- destination:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
# And 50% is routed to v2
weight: 50
We can apply this to the cluster with the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/3-progressive-traffic-shift-to-v2/vs-2.yaml
Now when we send traffic to the gateway, we should see half of the requests return version:v1 and the
other half return version:v2.
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v2
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v1
In practice, during this process it's likely you'll be monitoring some performance and business metrics to ensure the traffic shift isn't resulting in a decline in the overall quality of service. We can even leverage operators like Flagger to help automate this Gloo workflow. Gloo Enterprise integrates with your metrics backend and provides out of the box and dynamic, upstream-based dashboards that can be used to monitor the health of the rollout. We will save these topics for a future post on advanced canary testing use cases with Gloo.
Finishing the rollout
We will continue adjusting weights until eventually, all of the traffic is now being routed to v2:
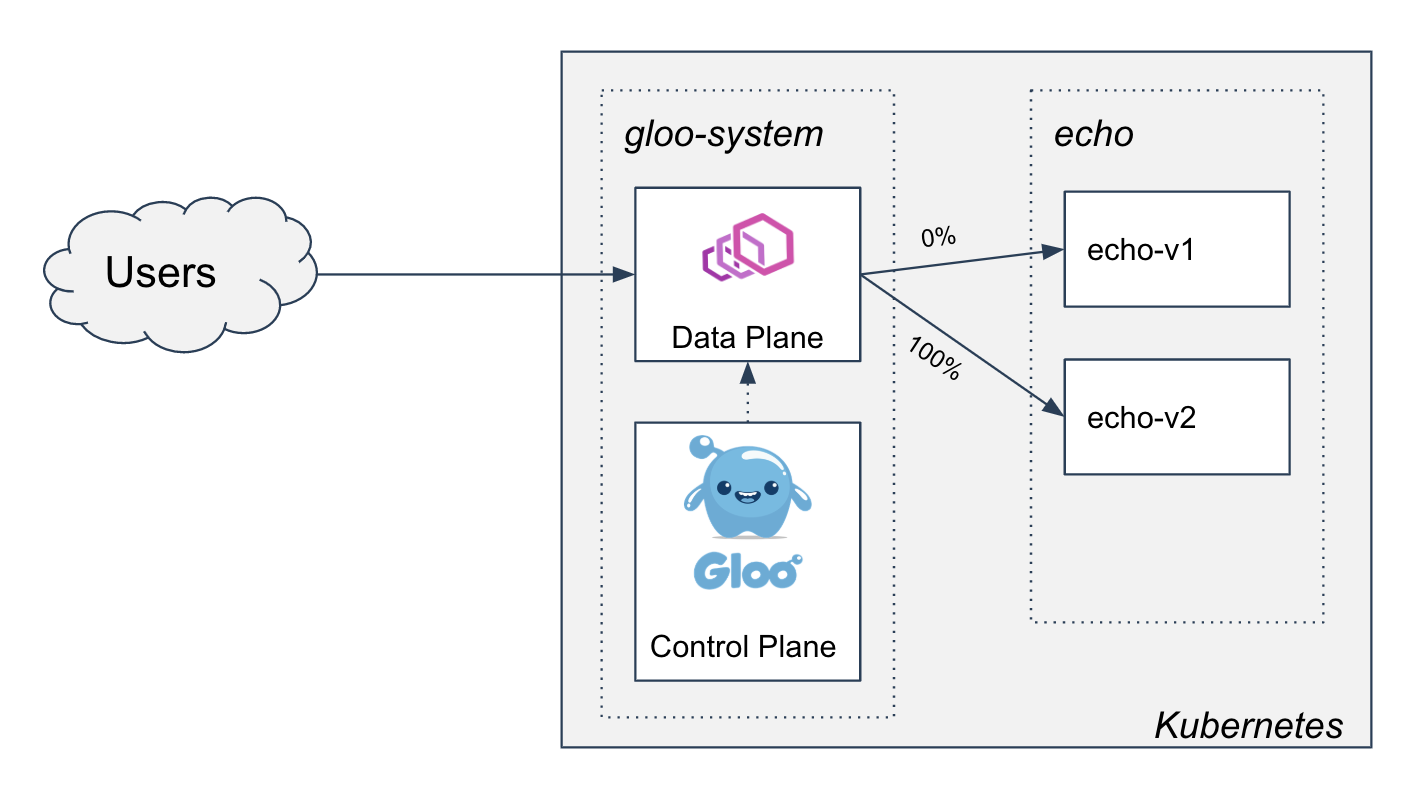
Our virtual service will look like this:
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- matchers:
- headers:
- name: stage
value: canary
prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
multi:
destinations:
- destination:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v1
# No traffic will be sent to v1 anymore
weight: 0
- destination:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
# Now all the traffic will be routed to v2
weight: 100
We can apply that to the cluster with the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/3-progressive-traffic-shift-to-v2/vs-3.yaml
Now when we send traffic to the gateway, we should see all of the requests return version:v2.
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v2
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v2
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v2
Decommissioning v1
At this point, we have deployed the new version of our application, conducted correctness tests using subset routing,
conducted load and performance tests by progressively shifting traffic to the new version, and finished
the rollout. The only remaining task is to clean up our v1 resources.
First, we'll clean up our routes. We'll leave the subset specified on the route so we are all setup for future upgrades.
apiVersion: gateway.solo.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
spec:
virtualHost:
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- matchers:
- prefix: /
routeAction:
single:
upstream:
name: echo
namespace: gloo-system
subset:
values:
version: v2
We can apply this update with the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/solo-io/gloo-ref-arch/blog-30-mar-20/platform/prog-delivery/two-phased-with-os-gloo/4-decommissioning-v1/vs.yaml
And we can delete the v1 deployment, which is no longer serving any traffic.
kubectl delete deploy -n echo echo-v1
Now our cluster looks like this:

And requests to the gateway return this:
➜ curl $(glooctl proxy url)/
version:v2
We have now completed our two-phased canary rollout of an application update using Gloo!
Other Advanced Topics
Over the course of this post, we collected a few topics that could be a good starting point for advanced exploration:
- Using the JWT filter to verify JWTs, extract claims onto headers, and route to canary versions depending on a claim value.
- Looking at Prometheus metrics and Grafana dashboards created by Gloo to monitor the health of the rollout.
- Automating the rollout by integrating Flagger with Gloo.
A few other topics that warrant further exploration:
- Supporting self-service upgrades by giving teams ownership over their upstream and route configuration
- Utilizing Gloo's delegation feature and Kubernetes RBAC to decentralize the configuration management safely
- Fully automating the continuous delivery process by applying GitOps principles and using tools like Flux to push config to the cluster
- Supporting hybrid or non-Kubernetes application use-cases by setting up Gloo with a different deployment pattern
- Utilizing traffic shadowing to begin testing the new version with realistic data before shifting production traffic to it
Get Involved in the Gloo Community
Gloo has a large and growing community of open source users, in addition to an enterprise customer base. To learn more about Gloo:
- Check out the repo, where you can see the code and file issues
- Check out the docs, which have an extensive collection of guides and examples
- Join the slack channel and start chatting with the Solo engineering team and user community
If you'd like to get in touch with me (feedback is always appreciated!), you can find me on the Solo slack or email me at [email protected].